Cold baths might shorten lifespan for seniors! Canadian researchers find it effective only in middle-aged men, while seniors may trigger inflammation. Rapamycin could reverse effects.
Temperature-Dependent Relationship of Autophagy and Apoptotic Signaling During Cold-Water Immersion in Young and Older Males
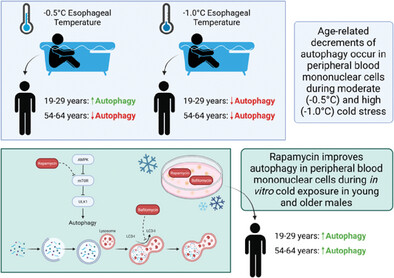
Autophagy is a crucial cytoprotective mechanism preventing the accumulation of cellular damage, especially during external stimuli such as cold exposure. Older adults poorly tolerate cold exposure and age-related impairments in autophagy may contribute to the associated reductions in cold tolerance. The purpose of this investigation is to evaluate the effect of different intensities of in vivo cold-water immersion and in vitro cold exposure on autophagic and apoptotic signaling in young and older males. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are isolated at baseline, end-cold exposure, and after 3 h of thermoneutral recovery. Additionally, PBMCs are treated with rapamycin and bafilomycin prior to in vitro cold exposure equivalent to in vivo core temperatures (35–37 °C). Proteins associated with autophagy, apoptosis, the heat shock response, and inflammation are analyzed via Western blotting. Moderate cold stress (0.5 °C decrease in core temperature) increased autophagic and heat shock protein activity while high cold stress (1.0 °C decrease in core temperature) augmented apoptosis in young males. In older males, minimal autophagic activation during both cold-water exposures are associated with increased apoptotic and inflammatory proteins. Although in vitro cold exposure confirmed age-related dysfunction in autophagy, rapamycin-induced stimulation of autophagic proteins underlie the potential to reverse age-related vulnerability to cold exposure.
Full Paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adbi.202300560
7 Likes
brand
#2
14C
https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adbi.202400111
The Effect of 7-Day Cold Water Acclimation on Autophagic and Apoptotic Responses in Young Males
Abstract
While cold acclimation can enhance thermoregulation in humans, the potential to improve cellular cold tolerance remains unknown. Thus, this work aims to evaluate the effect of a 7-day cold-water acclimation on the cytoprotective mechanism of autophagy in young males. Further, this work assesses changes in cellular cold tolerance by employing hypothermic ex vivo (whole blood) cooling prior to and following acclimation. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells are isolated before and after cold exposures on days 1, 4, and 7 of acclimation and following ex vivo cooling. Proteins associated with autophagy, apoptosis, the heat shock response, and inflammation are analyzed via Western blotting. Indicators of autophagic dysfunction paired with increased apoptotic signaling are prevalent at the beginning of acclimation. At the end of acclimation, autophagic activity increased while apoptotic and inflammatory signaling decreased. Although an elevated heat shock response is observed following cold exposure, this does not change throughout the acclimation. Further, improvements of autophagic activity are observed during ex vivo cooling along with a reduction of apoptotic signaling, albeit still elevated compared to basal levels. This work shows that 7-day cold acclimation elicits improvements in cellular cold tolerance in young males through enhanced autophagic responses concomitant with reductions in apoptotic signaling.14C
Neo
#3
Anyone know if it’s possible to do these autophagy tests? They seem to be based on blood tests?
Could great to optimize fasts, CR, ketosis, rapamycin protocols
brand
#4
The new study is at 14 degrees for young men. No idea how it affects other cohorts.